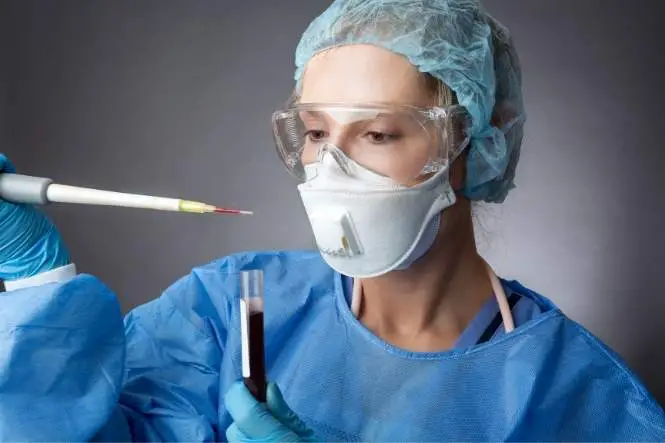
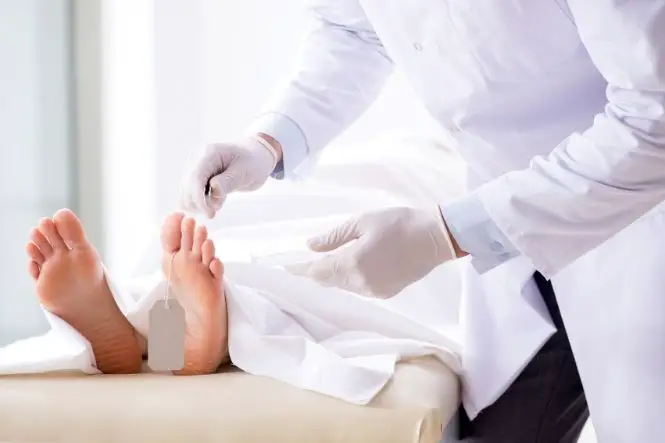
What is a Pathologist?
A pathologist is the senior doctor responsible for the performance of autopsies and for the determining as to how an individual died. This particular role within the forensic science sector is a demanding and sometimes harrowing job, which is not for those faint of heart. What a Pathologist Does Indeed …